The subcutaneous soft tissues are not typically involved. Neuropathic arthropathy Charcot joint can be defined as bone and joint changes that occur secondary to loss of sensation and is most often associated with.

Advanced Stage Of Neuro Osteo Arthropathy Charcot Foot On Download Scientific Diagram
Deformed humerus and glenoid does show defects mimicking Hill-Sachs posterolateral humeral defect and inferior glenoid Bankarts-like lesion.

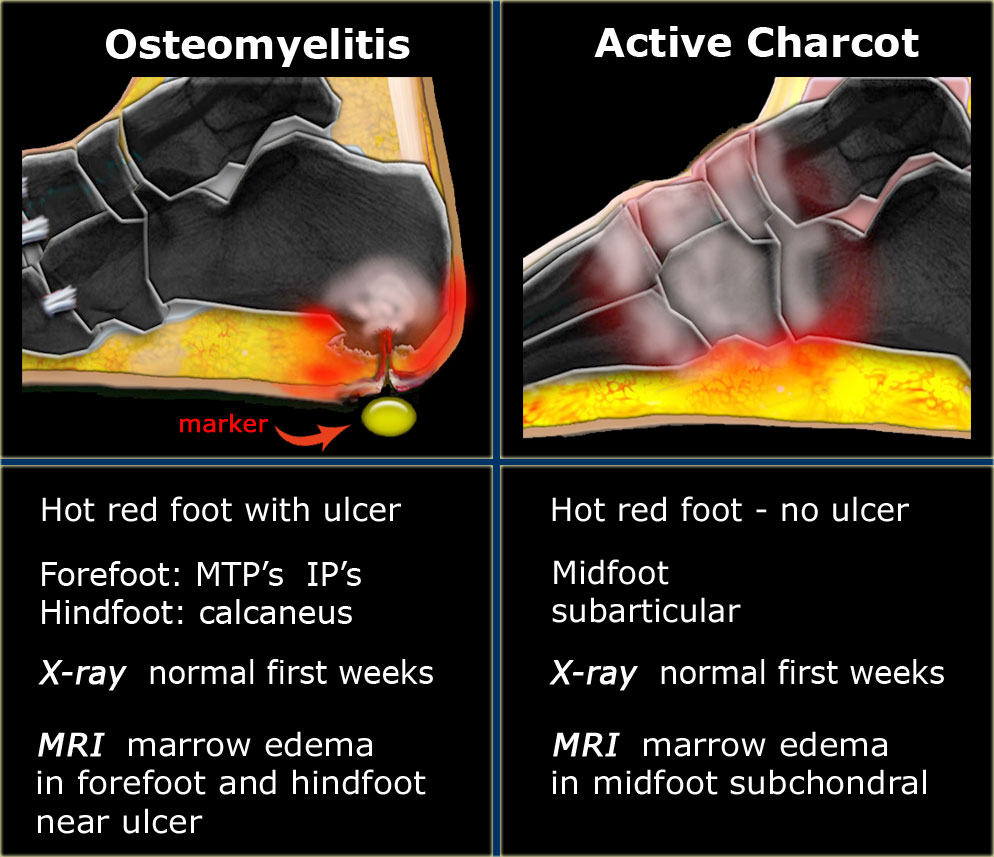
Charcot joint radiology ct. In this stage prompt diagnosis and immediate treatment is necessary to prevent further bone and joint. Computed tomographic CT changes of neuropathic osteoarthropathy of the spine are those of sclerosis and destruction of all three vertebral columns including destruction of the facet joints and can be important in distinguishing neuropathic osteoarthropathy from vertebral osteomyelitis which typically involves a single vertebral column 12. Unlike osteomyelitis Charcot neuro-osteoarthropathy is primarily an articular disease which is most commonly located in the midfoot.
There is also syringomyelia and mild cerebellar tonsillar herniation on spine images. T1 sagittal and axial and T1 fat sat post contrast sagittal images. The subcutaneous soft tissues are not typically involved.
The appearances at the T10-11 level are most in keeping with a Charcot joint spinal neuroarthropathy with this level being the susceptible site of hypermobility due to partial spinal ankylosis above and below. 6 Ds separating disorganization and dislocation Mnemonic. High signal within the L3-4 intervertebral disc corresponds to disc vacuum phenomenon on the CT.
These bony changes with mechanical deformities may yet be present and can be seen radiologically 913. In a study comparing 19 patients with proven disk space infection and 14 patients with spinal neuroarthropathy investigated by CT or MRI the best discriminators were intradiscal vacuum phenomena osseous debris facet joint involvement joint disorganization spondylolisthesis and dislocations and signal patterns on T2-weighted and gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted MRI. During early-stage Charcot foot CT does not play an important role for imaging since bone marrow and soft tissue changes can be better visualized using MRI.
It was first described by a French neurologist Jean-Marie Charcot in 1868. Charcot believed that the disease resulted from damage to central nervous system trophic centers that controlled bone and joint nutrition. Al-though the Charcot theory is no longer accepted joints affected by the disorder are still often re-ferred to as Charcot joints.
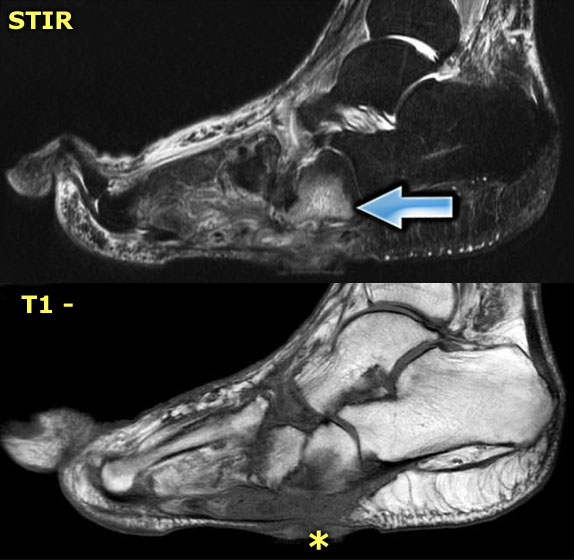
In the early stage radiography will not demonstrate bone abnormalities but MRI will show subchondral bone marrow edema. In the early stage radiography will not demonstrate bone abnormalities but MRI will show subchondral bone marrow edema. An anteroposterior AP radiograph of the left shoulder shows no discernible humeral head a very sharp margin to the end of the proximal humerus and ossific fragments projected within the confines of the shoulder joint capsule including a crescentic radiodensity projected lateral to the proximal humerusThe axial view shows the proximal margin of the extant.
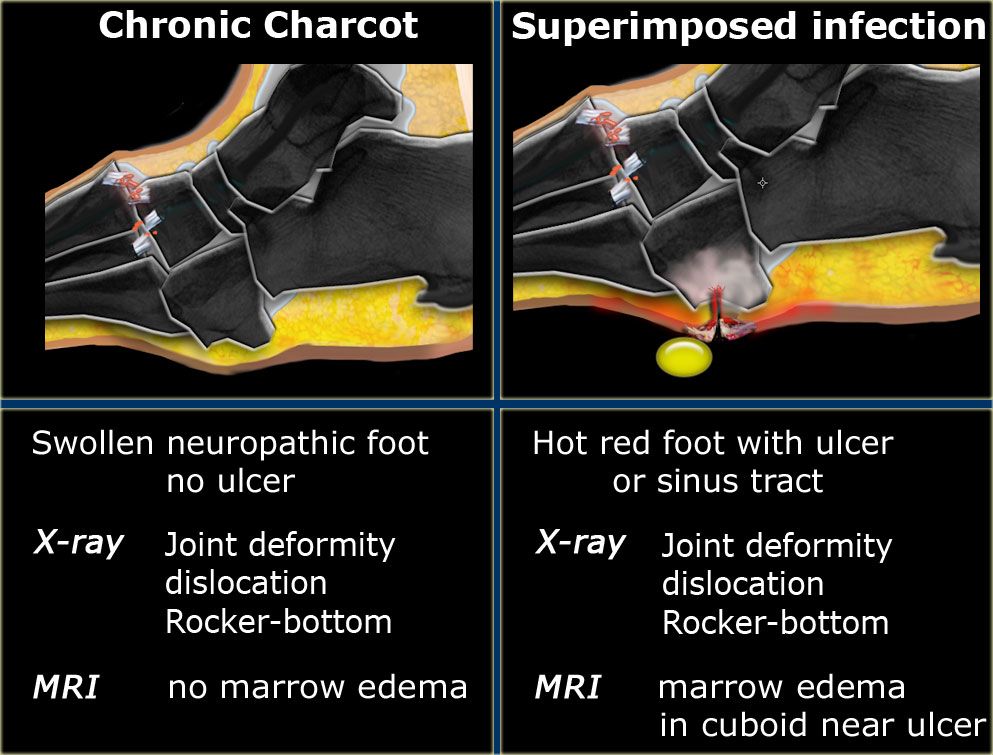
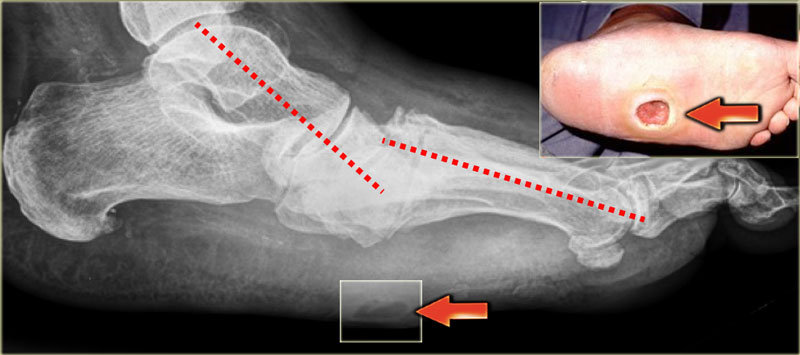
Subchondral generalized osseous destruction involving mid foot with reduced tarsometatarsal joint space tarsal marrow edema and exuberant osteophytosis. In the acute active stage Charcot neuro-osteoarthropathy shows rapid and progressive bone and joint destruction within days Figure 3. The radiographic features of a Charcot joint can be remembered by using the following mnemonics.
Unlike osteomyelitis Charcot neuro-osteoarthropathy is primarily an articular disease which is most commonly located in the midfoot. Chronic Charcot arthropathy with joint fluid and marrow edema. Sagittal T2 fat sat.
Ultrasound of Charcot ankle joint demonstrating a increased internal flow on colour Doppler in keeping with active synovitis surrounding echogenic internal loose bodies arrows confirmed as avulsed bony fragments on radiographs not shown and. Cidated by Jean Martin Charcot in 1868 1. Charcot neuropathic osteoarthropathy CN is a progressive disease affecting the bones joints and soft tissue of the foot and ankle most commonly associated with diabetic neuropathy.
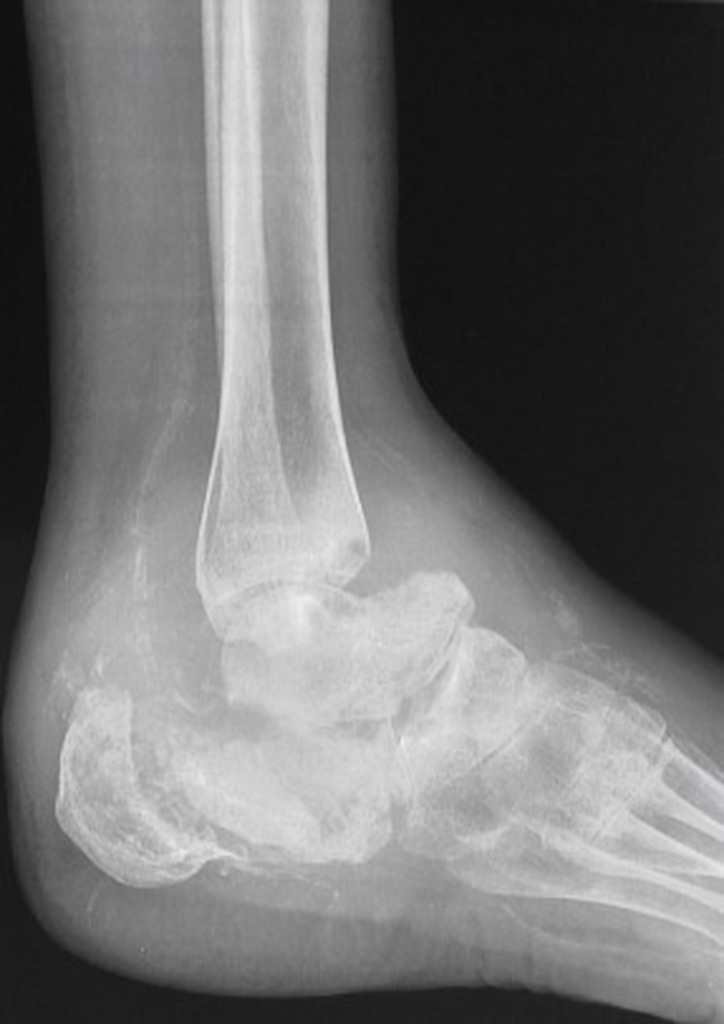
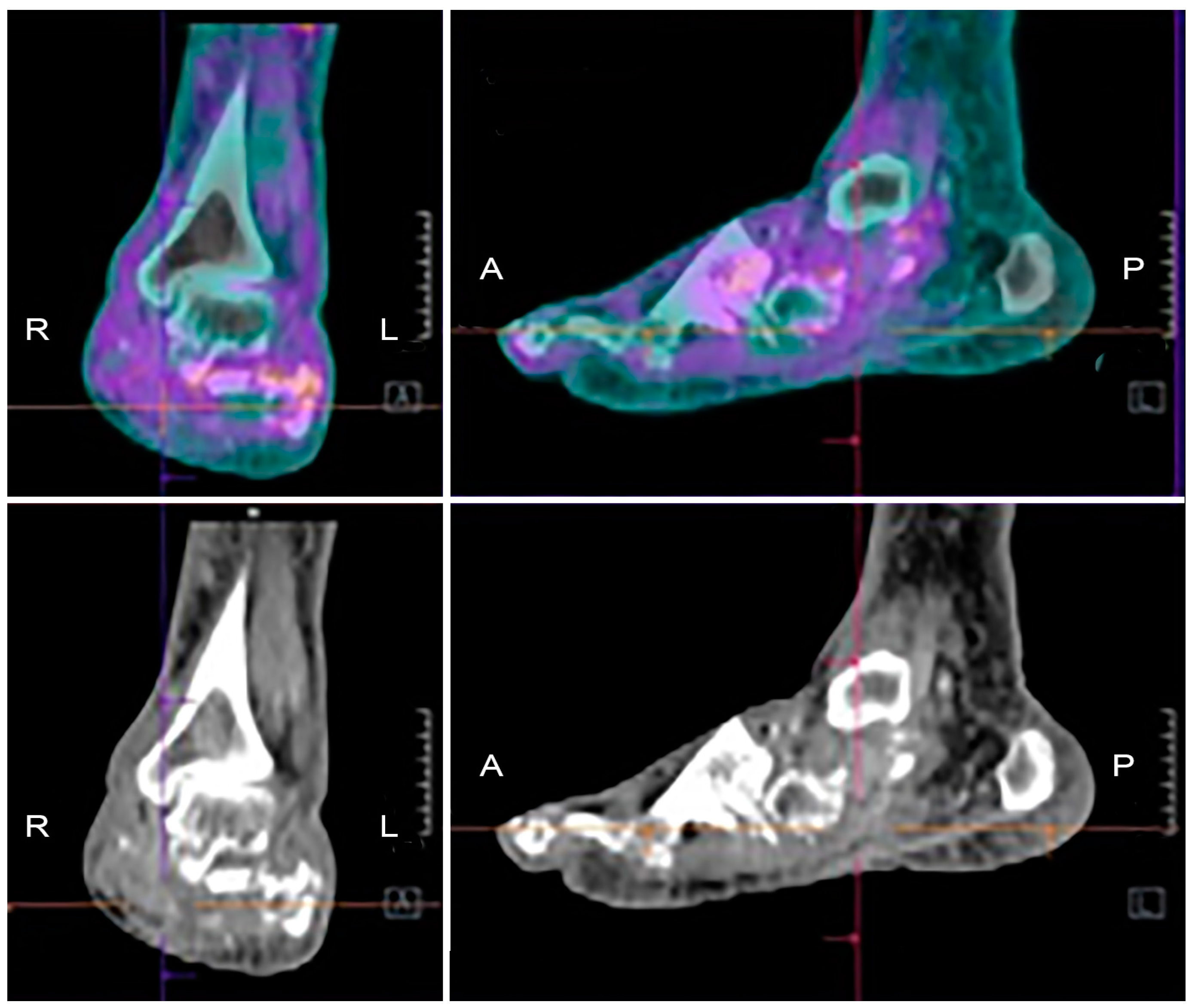
Computed tomography scan of the ankle in a patient with neuropathic arthropathy. No associated sinus tracks collections to suggest any secondary infection. Note the destruction of the articular surface disorganization of the joint and fragmentation.
Neuropathic arthropathy Charcot joint. Charcot joint also known as neuropathic arthropathy is a condition characterized by loss of sensation in the different joints of the body. However CT may be used in later-stage Charcot foot for better visualization of bony proliferations and consolidation or for surgery planning and treatment monitoring in patients with Ilizarov fixation 2.
Patients with diabetes complicated by CN have especially high morbidity frequency of hospitalisation and therefore significant utilisation of expensive medical resources. This case shows classical findings of Charcot Shoulder Neuropathic joint. Density change subchondral osteopenia or sclerosis Destruction osseous fragmentation and resorption Debris intra-articular loose bodies Distension joint effusion.
The Radiology Assistant Mri Examination

Charcot Joint Ankle Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
Advanced Stage Of Neuro Osteo Arthropathy Charcot Foot On Download Scientific Diagram

Role Of The General Surgeon In The Early Diagnosis And Treatment Of Charcot Foot Cirugia Espanola English Edition
Charcot Joint Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org

Neuropathic Charcot Arthopathy Of Spine Knee And Feet Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
The Radiology Assistant Mri Examination
The Radiology Assistant Mri Examination

A F Mri Examination Of Known Charcot Arthropathy Plain X Ray A Download Scientific Diagram

What The Radiologist Needs To Know About Charcot Foot Mautone 2015 Journal Of Medical Imaging And Radiation Oncology Wiley Online Library

The Radiology Assistant Mri Examination
Https Www Birpublications Org Doi Pdf 10 1259 Bjro 20180039

Pdf What The Radiologist Needs To Know About Charcot Foot
Neuropathic Joint Charcot Marie Tooth Disease Radiology At St Vincent S University Hospital

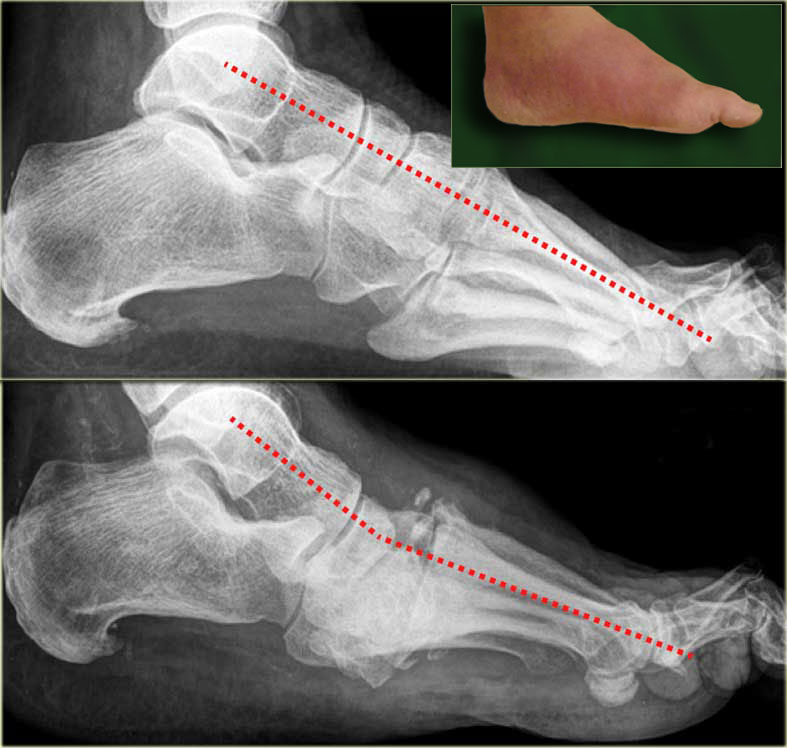
Lateral X Ray Of A Charcot Foot Deformity Showing A Dislocation Of The Download Scientific Diagram
The Radiology Assistant Mri Examination

Charcot Joint Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
The Radiology Assistant Mri Examination
Jcm Free Full Text Diabetic Foot Infections The Diagnostic Challenges Html
